更新时间:2024-08-16浏览量:64
Battery factory fire accident review: South Korea lithium battery factory fire, smoke engulfed the workshop for 15 seconds.
At around 10:31 a.m. local time on June 24, a serious fire broke out at a battery factory in Hwaseong, Gyeonggi Province, South Korea. So far, 23 people have been killed in the accident, including 19 Chinese citizens. At least 35,000 batteries may have been in the factory at the time of the fire. The battery factory involved (lithium battery manufacturer Aricell) mainly produces military lithium batteries, and a small number of civilian batteries are exported.

The head of the South Korean fire department said that after the initial investigation such as the analysis of on-site surveillance video, it took only 15 seconds from the white smoke of the lithium battery to the intense burning, and then to the smoke filled the entire working space. After the incident, although on-site employees tried to use fire extinguishers to put out the fire, they could not control the fire. It is initially believed that the victim inhaled a large amount of toxic fumes in a short period of time, resulting in suffocation and loss of consciousness. The South Korean government has not confirmed the specific cause of the fire, but a preliminary investigation showed that the lithium battery exploded during the process of testing the packaging.

A South Korean university fire and disaster prevention professor said that the battery factory accident caused many deaths and the reason is that the battery factory fire spread too fast, workers can not escape. "Because battery materials like nickel burn so easily, firefighting systems often don't have enough time to react compared to fires caused by other materials." Because lithium fires react violently with water, firefighters had to use dry sand to put out the blaze, which took several hours to bring under control, he said. However, after a fire is extinguished, it can still reignite without warning due to chemical reactions. "When the fire was on the second floor alone and there were so many casualties, it was because of toxic substances, not burns," he said.
With the occurrence of the above accidents, the fire safety problem of the battery factory once again triggered a high degree of social concern. According to statistics, there have been 28 battery factory fire accidents in South Korea in the past three years. South Korea is a major producer of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles and home to Hyundai Motor Group, the world's fifth-largest automaker, which is trying to shift from internal combustion engine vehicles to electric vehicles. This also means that the safety of lithium battery factories is facing a greater challenge. It is of great significance to carry out safety testing for the hidden safety risks of lithium batteries. Safety testing can evaluate the comprehensive performance of the battery, find the potential problems of the battery in time, and provide a reliable basis for the design and optimization of the battery. Safety testing can verify the safe use conditions of the battery and provide guidance for the packaging, transportation, storage and use of the battery. Safety testing can provide strong support for battery quality control and safety assurance, and protect the rights and safety of production personnel and consumers.
The necessity and significance of safety performance test of lithium battery
Although lithium batteries have many advantages, there are also certain safety risks. The positive and negative electrode materials and electrolytes of lithium batteries have certain chemical reactivity. When the battery encounters abnormal operations such as overcharge, overdischarge, and short circuit, it may cause thermal runaway reaction inside the battery, resulting in battery temperature rise, electrolyte leakage, battery expansion and other problems, and even fire or explosion in serious cases. In addition, lithium batteries may also have problems such as capacity attenuation and internal resistance increase during use, which may also lead to battery failure or cause safety accidents. In view of the safety risks existing in lithium batteries, safety testing is of great significance: (1) Safety testing can evaluate the comprehensive performance of the battery, find potential problems in time, and provide a reliable basis for the design and optimization of the battery. (2) Safety testing can verify the safe use conditions of the battery and provide guidance for the packaging, transportation, storage and use of the battery. (3) Safety testing can provide strong support for the quality control and safety of the battery, and protect the rights and safety of production personnel and consumers.
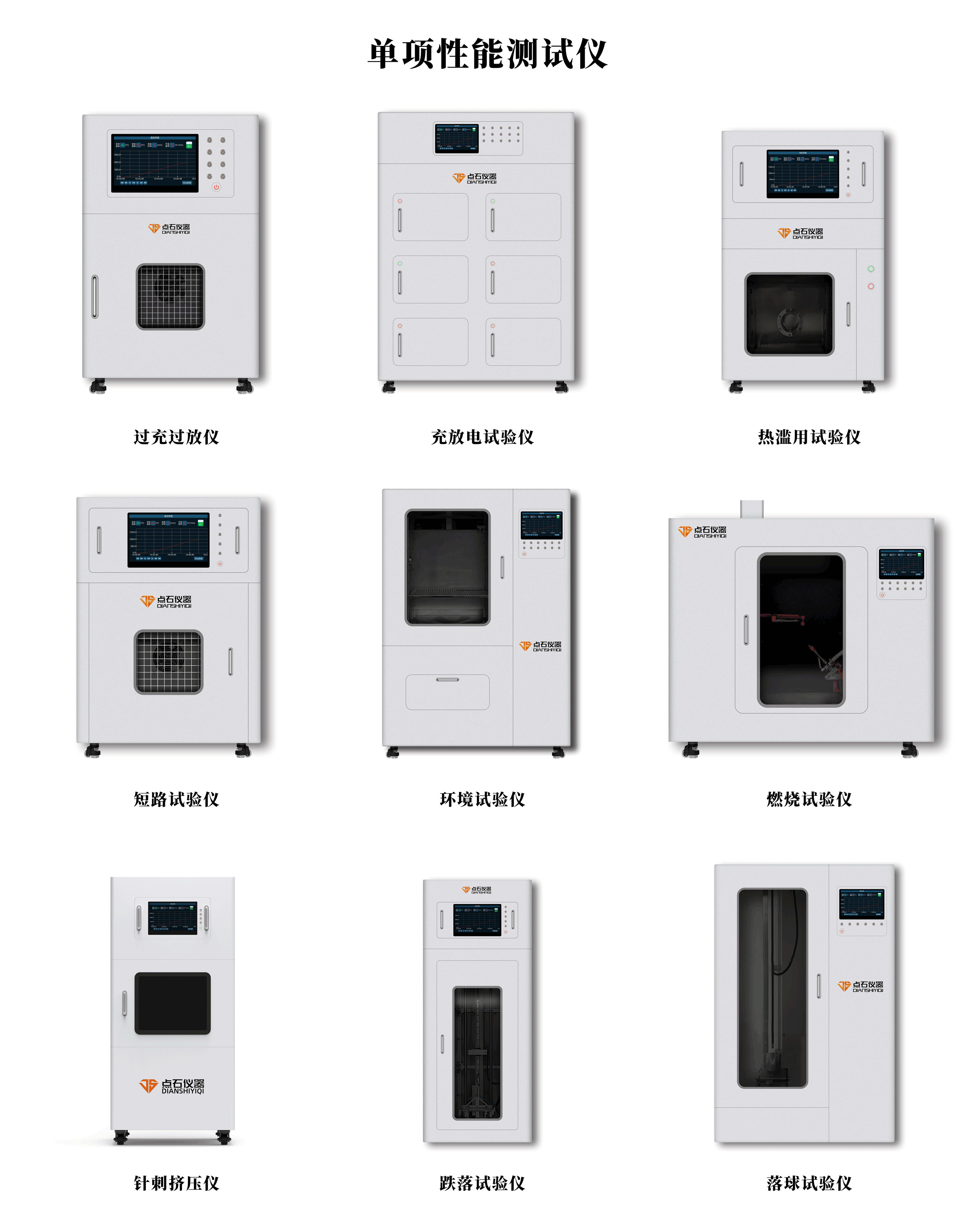
Point stone instrument focus on lithium battery safety performance test
As a battery test system solution supplier, Beijing Dianshi High-tech has established stable cooperative relations with battery manufacturers, testing institutions, universities and research institutes, and has independently developed and successfully delivered a number of battery comprehensive/single performance test equipment (which can meet the comprehensive performance test needs of scientific research grade batteries). It provides a convenient, reliable and efficient experimental platform for the safety performance test of lithium batteries.
# Lithium battery comprehensive performance tester
01 Battery comprehensive performance experiment room
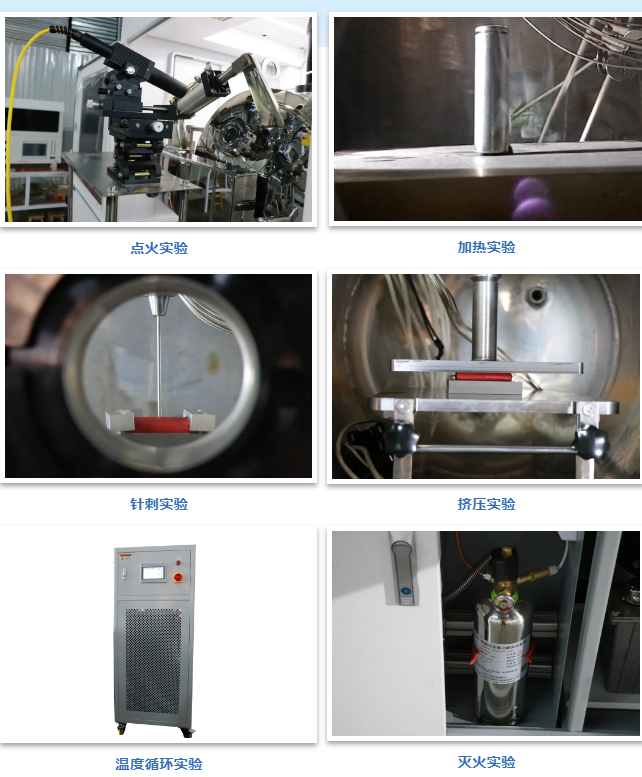
The battery comprehensive performance laboratory can realize the coupling of a variety of environmental factors (temperature, pressure, atmosphere, etc.), and carry out a variety of tests on the battery (acupuncture, extrusion, overcharge, overdischarge, short circuit, temperature cycle, ignition, fire extinguishing), which is used for the comprehensive performance test of single batteries and small battery modules.
(1) High temperature environment
Overall maximum ambient temperature: 100℃
Heating rate: 1℃/min
Maximum temperature of local table: 600℃
Maximum temperature rise rate: 10℃/min
According to standards: GB/T 2423.2-2008, IEC60068
(2) Low temperature environment
Minimum temperature: -50℃
Cooling rate: 1℃/min
According to standards: GB/T 2423.1-2008, GB/T 38031-2020
(3) High altitude environment
Minimum air pressure: 1kPa (A) (approximately 31200m above sea level)
Vacuum time: ≤9min
According to standard: GB/T 31467.3-2015

Test items

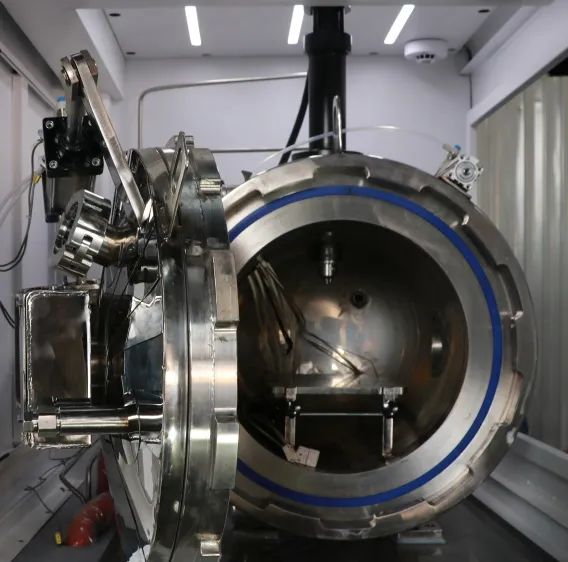
02 Walk-in integrated laboratory module

The walk-in integrated laboratory room can build a composite experimental environment (high temperature, low temperature, high altitude, salt spray) for temperature cycle experiments, corrosion resistance experiments, reliability experiments of large parts, and thermal runaway experiments of batteries.
# Lithium battery single performance tester